In this lesson, we will learn:
- Meaning of translational equilibrium
- Solving problems involving translational equilibrium
Notes:
- An object can undergo translational motion (motion that changes its position) and rotational motion (motion that changes its angle).
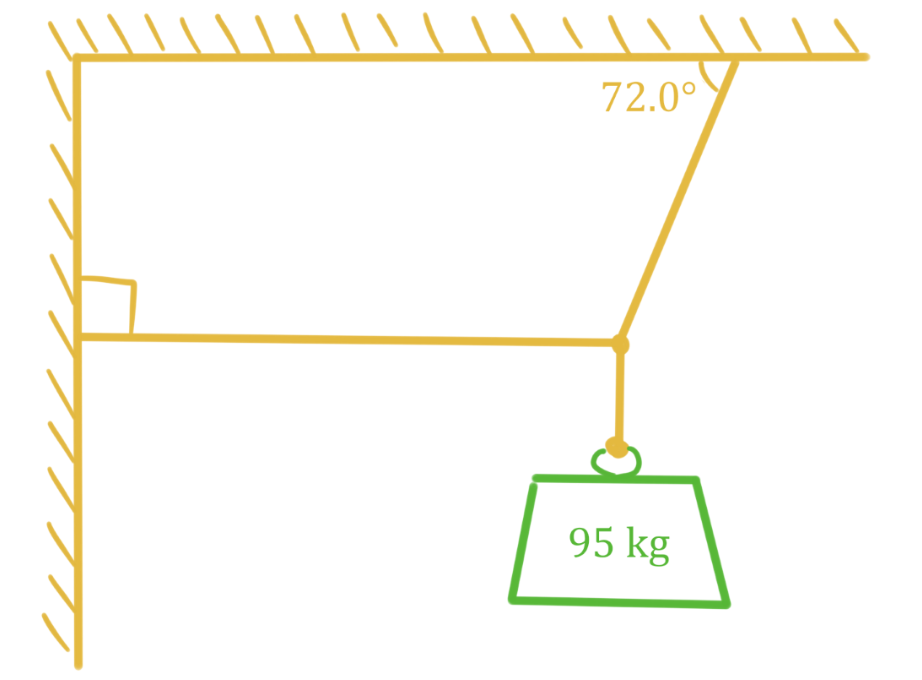
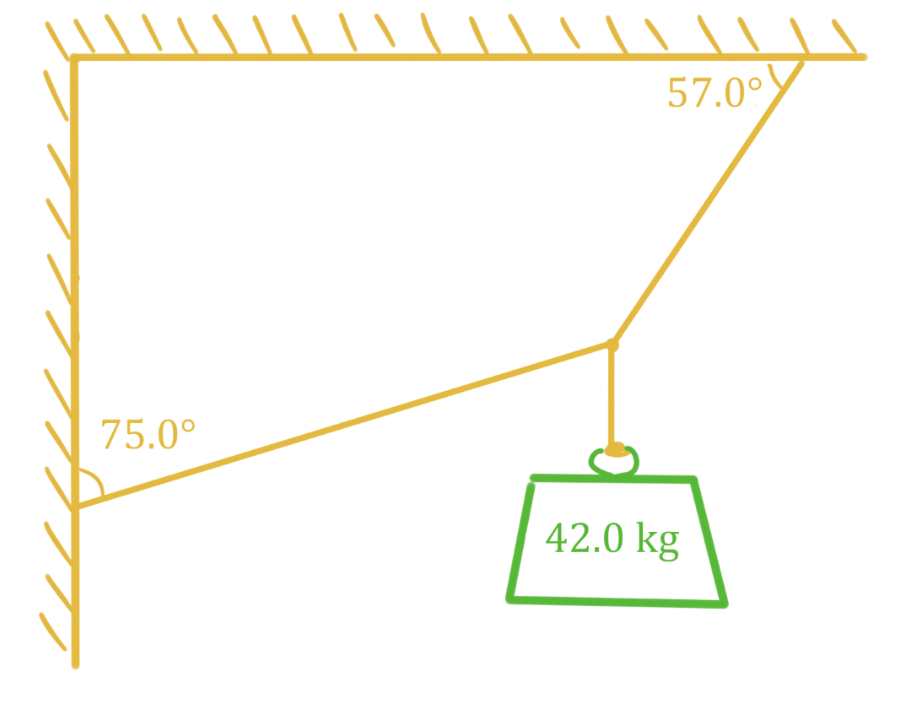
- An object is in translational equilibrium if the velocity of its translational motion is constant. An object that is not moving or an object that is moving in a straight line at a constant velocity would be considered in translation equilibrium. To be in translational equilibrium, the net force acting on the object must be zero (recall Newton's first law: if no unbalanced forces act on an object, it does not accelerate).
or equivalently:
and
sum of all forces, in newtons (N)
sum of all force components in x direction, in newtons (N)
sum of all force components in y direction, in newtons (N)