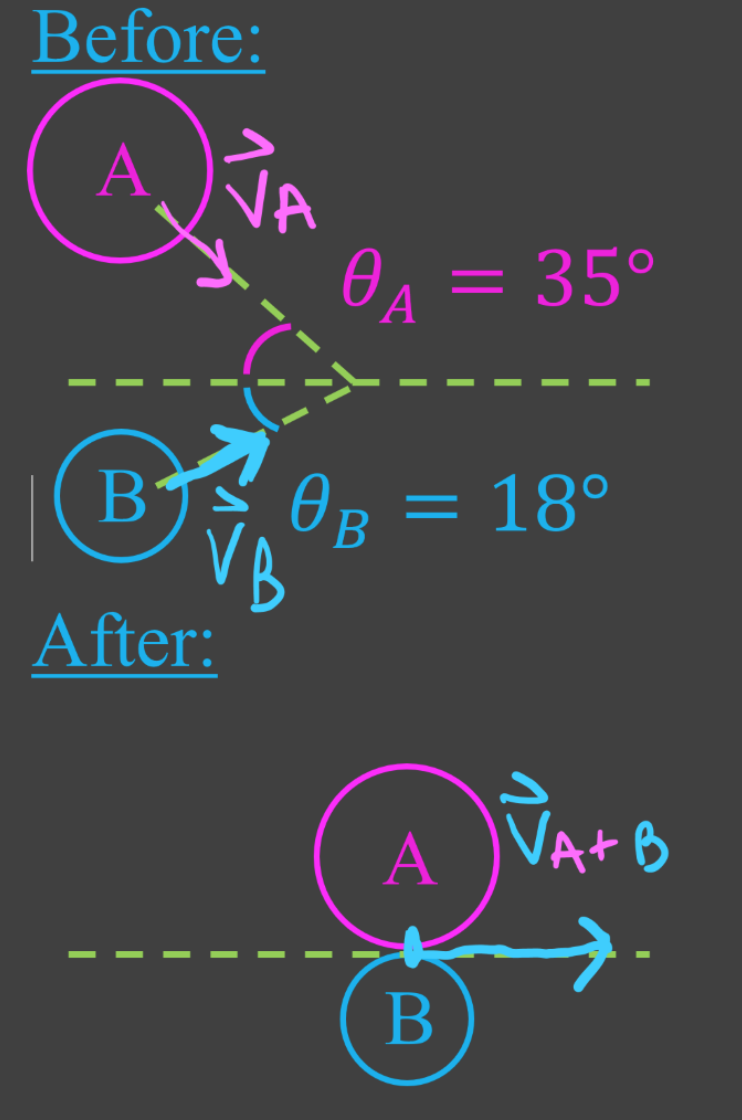In this lesson, we will learn:
- Review of conservation of momentum
- Vector nature of momentum and conservation of momentum
- Problem solving with conservation of momentum in two dimensions
Notes:
- Momentum is a conserved quantity and a vector.
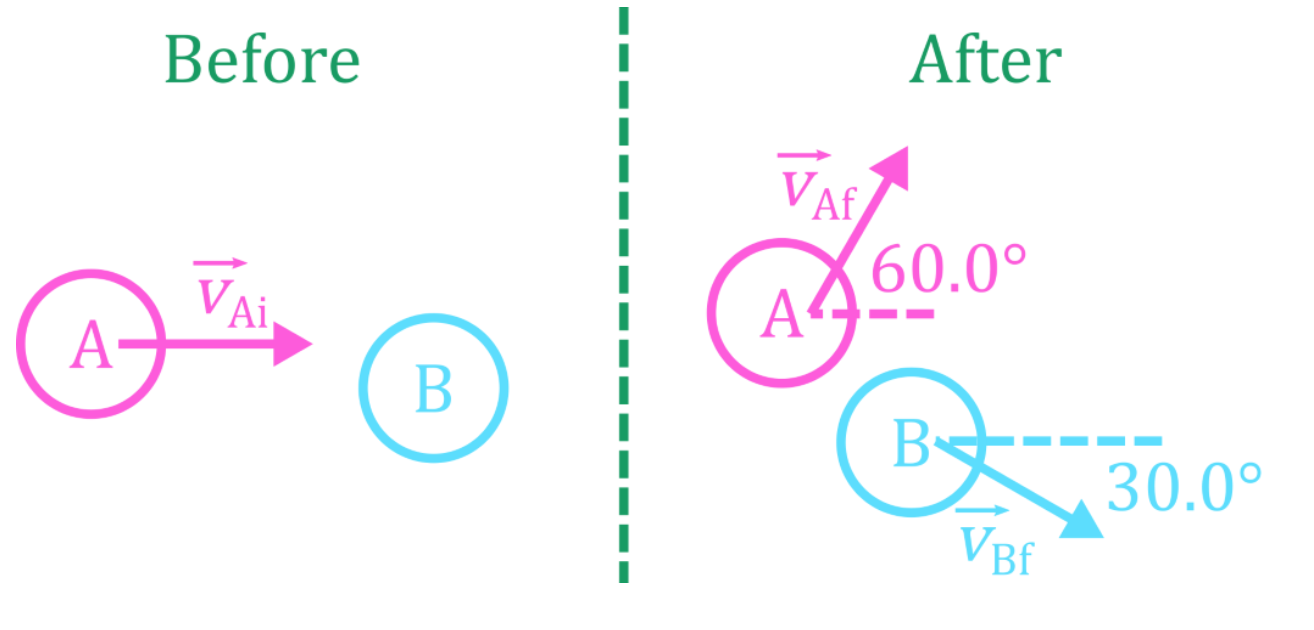
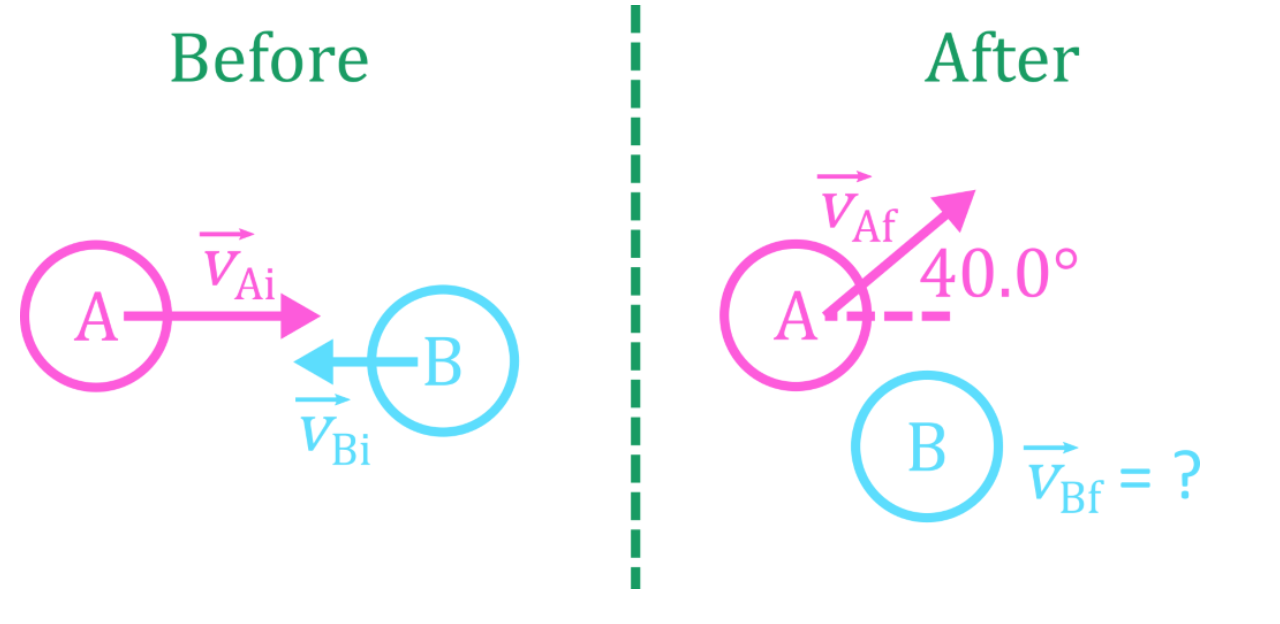
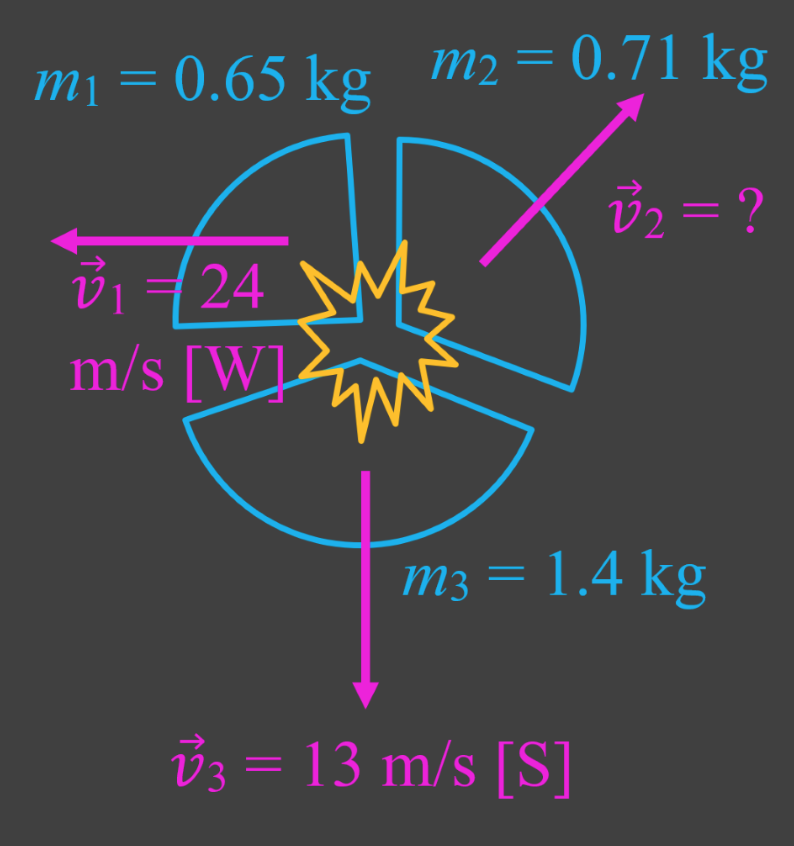
- In a collision between a set of objects, total momentum of the objects before collision = total momentum after collision.
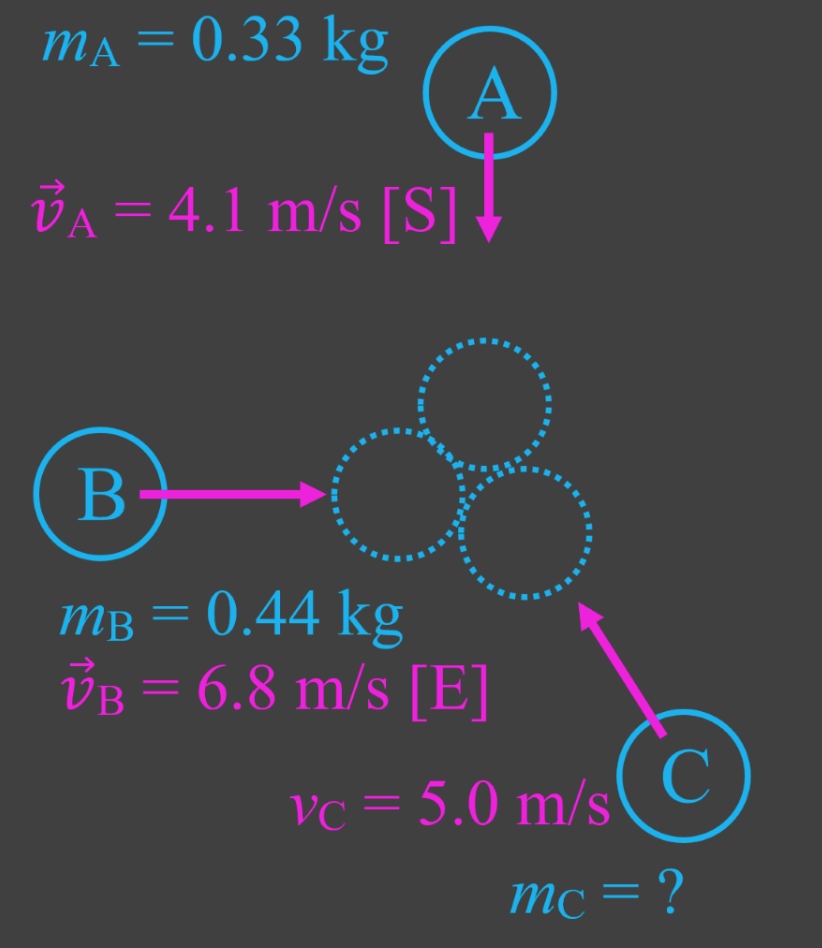
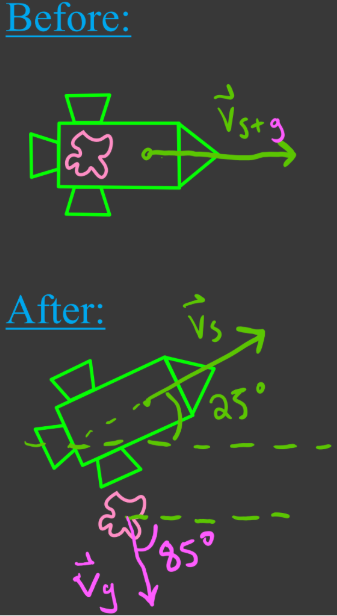
- When using conservation of momentum on objects that move in two dimensions, use vector addition (tip-to-tail method).
Momentum
momentum, in kilogram meters per second (kg∙m/s)
mass, in kilograms (kg)
velocity, in meters per second (m/s)
Impulse
impulse, in newton seconds (N∙s)
force, in newtons (N)
time, in seconds (s)
Conservation of Momentum
initial momentum, in kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s)
final momentum, in kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s)
Law of Sines
a,b,c: length of sides a,b,c
A,B,C: angles opposite sides a, b, c
Law of Cosines