Gradient intercept form: y = mx + b
0/3
Intros
Lessons
- Overview: Slopes of lines
- What is Slope intercept form?
- What is so important about it?
- Slope intercept form VS. General form VS. Slope-point form
0/11
Examples
Lessons
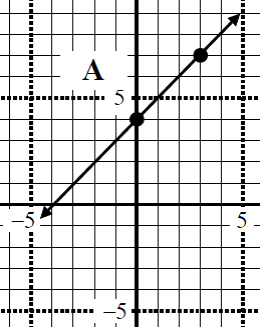
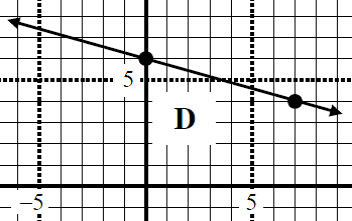
- Determine the Slope-Y-int form from the graph.
- Determine the slope, Y-int, domain, and range of the following linear function.
- Given the slope & Y-Int, write the equation in the slope -intercept form
- A point passes through an equation of . Find "".
- A point passes through an equation of . Find "".
- Given two points through a line, find the slope-intercept form