In this lesson, we will learn:
- What is impulse?
- Derivation of impulse from Newton's second law
- Impulse equations, units
- Problem solving with impulse and momentum
- Problem solving with F vs t graph
Notes:
- Impulse is change in an object's momentum.
- To change an object's momentum, an impulse must be given to that object. An example would be kicking a soccer ball (an impulse) to set it into motion (give it momentum).
- An impulse is defined as a force that acts on an object for a period of time.
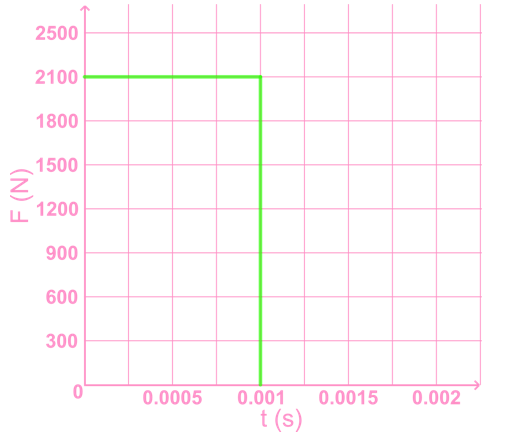
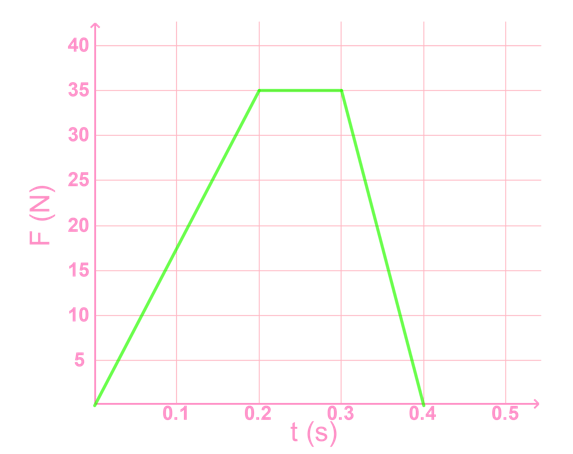
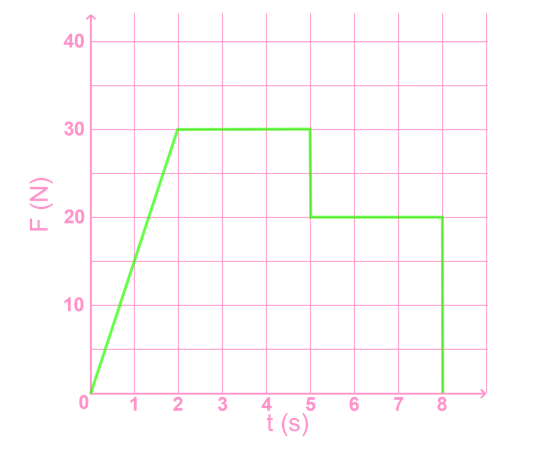
- In a graph of force vs. time, the area under the graph is impulse.
Momentum
momentum, in kilogram meters per second (kg∙m/s)
mass, in kilograms (kg)
velocity, in meters per second (m/s)
Impulse
)
impulse, in newton seconds (N∙s)
net force acting on an object, in newtons (N)
the length of time for which the force acts, in seconds (s)
change in momentum of an object, in kilogram meters per second (kg∙m/s)