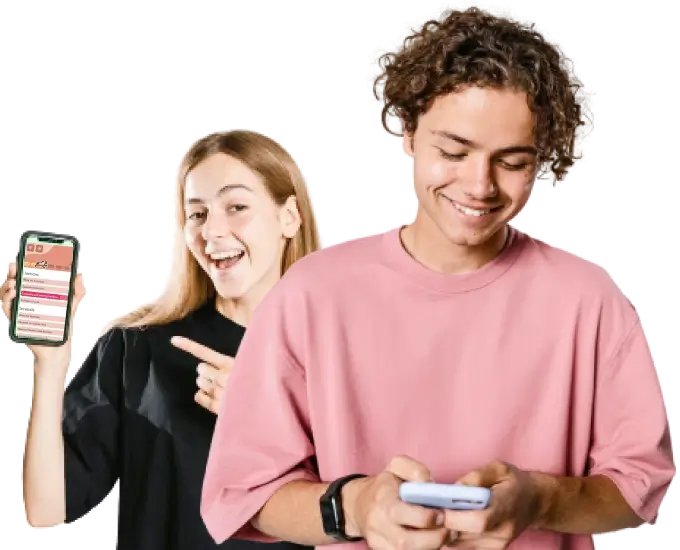
Ace Your Year 12 Maths Finals
Step-by-step solutions for exam success and university prep

📈
Final exam scores improve 10-15%
✨
University preparation
💡
Advanced concept mastery
📚
Graduate with confidence

Step-by-Step Solutions
Master advanced functions, calculus, and applications

Perfect Curriculum Match
Aligned with National Curriculum requirements

Guaranteed Results
Most students improve one letter grade in 4-6 weeks
Year 12 Maths Topics