
Antiderivative of tanx
The antiderivative of tanx is perhaps the most famous trig integral that everyone has trouble with. This is because it requires you to use u substitution.
What is the antiderivative of tanx
Let us take a look at the function we want to integrate.
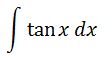
You may be asking yourself, how am I suppose to use u substitution? First, notice that tanx can be changed to sinx over cosx. In other words,
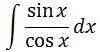
Now we are able to use u substitution.
Let u=cosx. Then we can say that du=-sinx. Note that multiplying both sides by a negative signgives -du=sinx. Thus, substituting will give us the following:
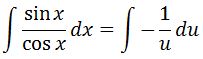
Now we can factor the negative sign out of the integral, which will give us:
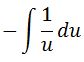
Now this leads to the question, how do I take the antiderivative of 1/u? Well it is exact same thing as taking the antiderivative of 1/x. The integral of 1/x is just the natural log of |x|. In other words,
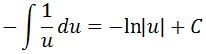
Always never forget to add the constant c because you are taking the antiderivative! Lastly, don't forget that originally the integral was in terms of x. So we need to change our antiderivative in terms of x. Recall that u=cosx, so substituting back will give:
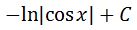
which is the integral of tanx.
Since we are on the topic of trig integrals, why don't we take a look at the integrals of some trig functions? Since tanx is a combination of sinx and cosx, why don't just find the antiderivative of them separately?Let us go ahead and find the antiderivative of sin and the antiderivative of cosx.
What is the antiderivative of sin
A lot of people just memorize that the antiderivative of sinx is simply –cosx. But how exactly does one derive that? There are a couple ways to illustrate this, but I will show you 2 methods.
Method 1:Backtrack by using derivatives
Instead of finding the antiderivative explicitly, our goal would be to find a function whose derivative is sinx. If the function's derivative is sinx, then it must be true that the antiderivative of sinx will give back that function. Okay, that sounds perfect. What function should we try? Let
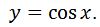
Notice that the derivative of this would be:
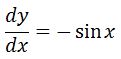
See that we are really close, but instead of sinx we have –sinx. How can we get rid of the negative? How about taking the function that we have and add an extra negative sign? This might lead to having the derivative to have two negatives, and it will become a positive. If we do that then let
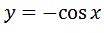
Now the derivative of this would be:
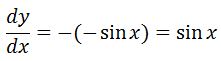
This is perfect! We have that the derivative is sinx, therefore our function is the antiderivative of sinx. Hence, the anti-derivative of sinx is
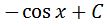
Again, don't forget to add the constant c.
Now that is a great way to finding antiderivatives, but some integrals may require a lot of guessing. What is a better way to find the antiderivative of sin? This leads us to the next method:
Method 2: Use Moivre's Theorem
This method can be pretty confusing if you do not know how to use complex numbers. So skip this method if you do not know Moivre's Theorem. Notice that according to Moivre's Theorem, we have that
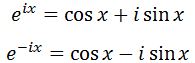
Adding these two equations gives:
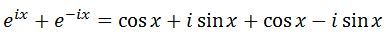
Simplifying the right side leads to:
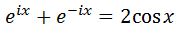
Thus dividing both sides by 2 will lead to:
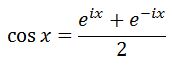
We will use this later. Now, instead of adding both equations, let us subtract these two equations.
Subtracting these two equations will give us:
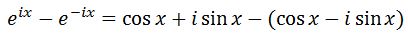
Simplifying the right side will give us:
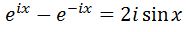
Isolating sinx by dividing by 2i will lead us to have:
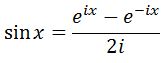
What are we going to with this? Well instead of taking the antiderivative of sin, we will take the antiderivative of what we see in the right hand side of the equation. This is because they are exactly equal. Therefore their antiderivatives should lead to the exact same answer. Hence, let's evaluate
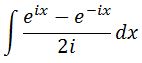
First, let us make this easier by factoring 1/2i out of the integral:
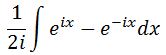
Now evaluating the integral will give us:
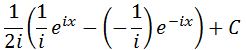
Simplifying gives:
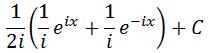
Notice that factoring 1/i out of each term and multiplying it with 1/2i gives:
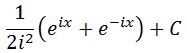
Since i^2=-1, then
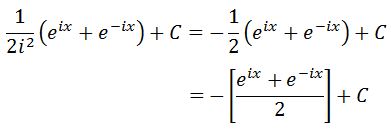
Notice from our equation earlier that:
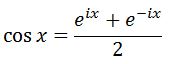
Hence substituting with this will lead us to have our final answer:
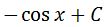
which is the antiderivative of sin. These are the two methods in finding the antiderivative of sin. Now let us move on to finding the antiderivative of cosx.
What is the antiderivative of cosx
Again, people memorize that the antiderivative of cosx is sinx. However, let's show that it is true by using the two methods we have mentioned earlier.
Method 1:Backtrack by using derivatives.
Let's find a function whose derivative is cosx. Why don't we say that:
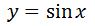
This is a great suggestion since we know that the derivatives of sin and cos are related. Now taking the derivative of this will give me:
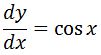
Notice that the derivative already gives cosx. This is great because we don't need to make any adjustments to the function. Hence, we know that the antiderivative of cosx is:
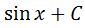
Once again, do not forget to add the constant C.
Now if you do not want to guess and test, then we can use method 2.
Method 2: Use Moivre's Theorem
From earlier we know that:
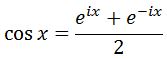
Again, instead of integrating cosx, we are instead going to find the antiderivative of the right hand side of the equation (since they are exactly equal). Thus, let us evaluate
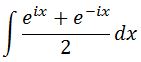
Factoring 1/2 out of the integral will give us:
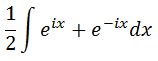
Evaluating the integral leads to:
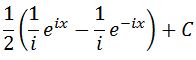
Distributing 1/2 to each term gives:
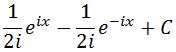
Now we can rewrite this equation to
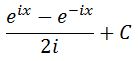
Coincidentally, we knew from earlier that:
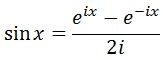
Hence substituting this will give us
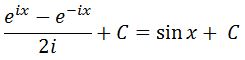
which is the antiderivative of cosx. If you want to look at more antiderivatives of trig functions, then I suggest you look at the second section of this article "Antiderivative of trig functions"
Now if you're wondering if it is possible to take the antiderivative of inverse trigonometric functions, then the answer is yes. Since we've found the antiderivative of tanx, sinx, and cosx, why don't we find the antiderivative of their inverses? Let's take a look at arctan.
What is the antiderivative of arctan?
In order to find the antiderivative of arctan, we must know what the derivative of arctan is. If you do not know what it is, we recommend you to look at this article below. It gives a step by step solution in finding the derivative of arctan.
Now to find the antiderivative of arctan, let's set up our integral:
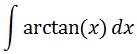
The hard part is noticing that we need to use integration by parts. Recall that the integration by parts formula is:
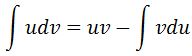
We set
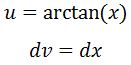
Thus taking the derivative of u and integrating dv will give us:
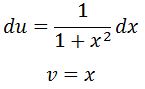
Hence using the integration by parts formula will give us:
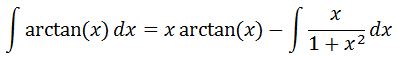
If you are not familiar with integration by parts, check out the lessons on it.
Now in order to integrate x/(1+x^2), we need to use u substitution. Let u=1+x^2. Then we will have du=2xdx. Therefore ½ du=xdx. Substituting this will give
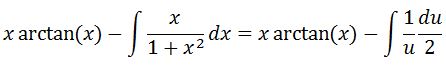
Simplifying leads to:
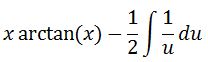
Integrating gives:
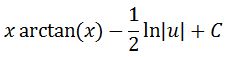
Notice that we substituted with u=1+x^2 earlier, so switching u back to in terms of x will give us:
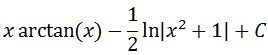
Hence we can conclude that:

Now if are interested in finding the antiderivative of arcsin and arccosx, then take a look at these links here. They show a step by step solution in finding these antiderivatives.
http://www.ditutor.com/integration/integral_arccos.html
http://www.ditutor.com/integration/integral_arcsin.html
Notice that the technique is very simple to the antiderivative of arctan. All of them require the use of integration by parts.
Antiderivative of trig functions
In this section, we will focus on finding the antiderivative of trig functions that are reciprocals of tanx, sinx, and cosx, well as trigonometric functions which would require half angle identities to integrate. Note that reciprocal trig functions and inverse trig functions are NOT the same. Hence inverse trig integrals are different from reciprocal trig integrals. Inverse trig integrals are the ones we did earlier! One thing to also note is that a lot of antiderivatives in this section require you to know derivative of trig functions as well. So make sure you know them well before tackling these questions. If you are not very good at them, we recommend you to look at this link to practice!
What is the antiderivative of secx?
There are a few ways to do this, but the best way is to use a shortcut. For this shortcut, we will need to know what the derivative of sec is. If you do not know what it is, you can refer to this link.
https://socratic.org/questions/what-is-derivatives-of-y-sec-x
This link gives a step by step solution for the derivative of sec.
First, let us set up our integral for the antiderivative of secx.
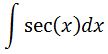
Next, we are going to multiply the integrand by secx +tanx / secx + tanx. So we will give us:
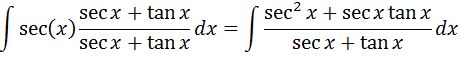
What was the reason for doing this? Didn't you just made it even more complicating? If you noticed, there is actually a relationship between the denominator and the numerator. The derivative of the denominator is the numerator! Taking that into consideration, we just use the u substitution technique. In other words if we set u=secx + tanx, then du= sec^2x +secxtan x dx. Hence we see that
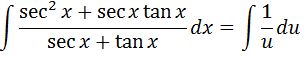
We can now easily integrate, which will give us:
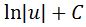
Recall that u=secx + tanx, so converting u back in terms of x will give us:
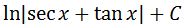
which is the integral of secx. This shortcut is really neat, but what if I were to take sec to the power of 2? Does it make it harder to integrate? It is actually easier!
What is the antiderivative of sec^2?
Again, I will show 2 methods.
Method 1: Backtrack by using derivatives.
Let's find a function whose derivative is sec^2x. Let us say that:
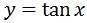
This is a great suggestion since we know that the derivatives of tan and sec are somewhat related. Thus, taking the derivative gives us:
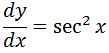
Notice that the derivative already gives sec^2x. Hence we do not have to make adjustments to the original function, and we know that the antiderivative of sec^2x is:
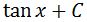
Now if you do not want to guess and test, then we can use method 2.
Method 2: Integrate directly with trig identities
Integrating sec^2 x directly actually requires us to know some trig identities. The one we will be using is:
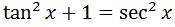
Now setting up our integral, we have:
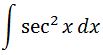
Using the trig identity that I have mentioned earlier, we can change our integral to
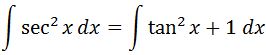
We know that tanx = sinx / cosx and we can split an integral into two, so we can modify our integral such that:
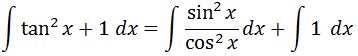
Splitting an integral into two is one of the properties of integrals. If you are not familiar with the properties very well, I recommend you check this link out.
http://www.math.pitt.edu/~sparling/052/23052/23052notes/23052notestojan14th/node6.html
Now the second integral is easy to evaluate, but the first one is a little bit harder. For the first part, we will need to use integration by parts. Let u=sinx and dv=sinx/cos^2x dx. Then
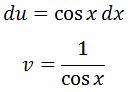
Recall the integration by parts formula is:
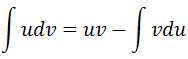
So plugging everything in gives:
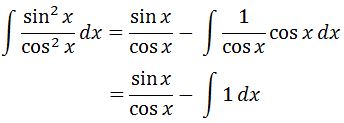
Now putting the first and second part together we will have
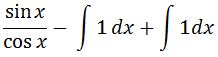
Notice that the integrals cancel out without even having to evaluate them. In addition, we know that sinx / cosx is tan x. So in conclusion,
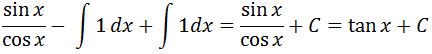
which is the integral of sec^2. Now let us take a look at other reciprocal functions.
What is the antiderivative of cscx?
You may try to use the method that involves backtracking using derivatives, but you may find that to be a little difficult. Instead, I am going to use a similar trick which I used earlier for the integral of secx. Setting up the integral of cscx we have:
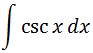
We are going to multiply the integrand by cscx + cotx / cscx + cotx. Doing so will give us:
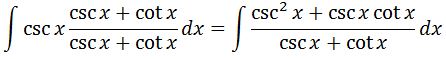
You may see a relationship between the denominator and numerator, but it is not exactly how we want it. This is because the derivative of the denominator csc x + cot x is –csc^2 x –csc x cot x. If you were to compare this with the numerator, then we see that we are missing two negative signs. Hence we need to change our integral to this:
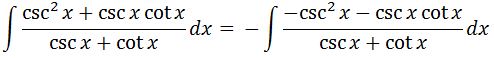
Now that the derivative of the denominator matches the numerator, we can begin using u-substitution. We set u= cscx +cotx and du = -csc^2 x – csc x cot x dx, so that
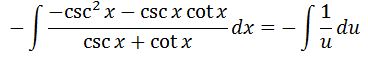
Now we can evaluate the integral, which gives us:
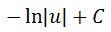
Again changing u back in terms of x will give us the final answer:
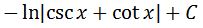
Now you may wonder again, would changing the power of csc make the integral even harder to compute? Not at all!
What is the antiderivative of csc^2?
Again I will show two methods. You may notice that these two methods are the exact same as the antiderivative of sec^2. In fact, the process is very similar too!
Method 1:Backtrack by using derivatives.
Again, we have to find a function whose derivative is csc^2 x. Again, if the function's derivative iscsc^2 x, then it must be true that the antiderivative of csc^2 will give back the exact same function, plus a constant. So let
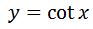
Why cot x? This is because the derivative of cot x and csc x relate to one another. So it is a good idea to have a function that has the term cot x. Notice that the derivative of this would be:
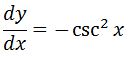
See that we are really close, but instead of csc^2 x we have –csc^2 x. How can we get rid of the negative? Add an extra negative sign to cancel the other negative sign!So let us add a negative sign to our function from earlier. This gives us
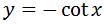
Now the derivative of this would be:
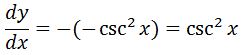
Perfect! We have the derivative exactly as we wanted. Hence, it must be true that the anti-derivative of csc^2 (going backwards) is
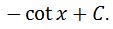
Now we might as well finish up by finding the antiderivatives of cotx and cot^2x.
Method 2: Integrate directly with trig identities
To integrate this, we will need the following trig identity:
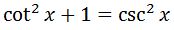
So setting up the integral we have:
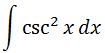
Using the trig identity that we learned above, we can convert the integral to:
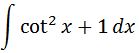
We know that cotx = cos x / sin x, and we can split the integral into two parts so that:
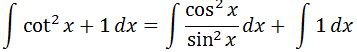
Again, the second part of the integral is easy to integrate, but the first part would require u-substitution. For the first part, let
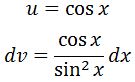
Then deriving u and integrating dv gives:
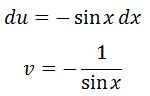
Plugging it in the integration by parts formula will give us:
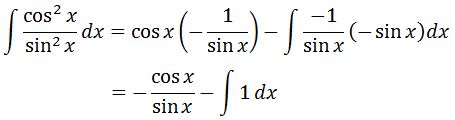
Combining the first part and second part of the integral gives:
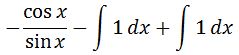
Again we can see that cotx = cos x / sin x, and also the integrals cancel each other out. Hence we conclude that
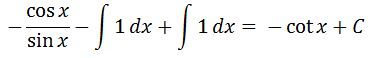
which is the integral of cscx. Now let us take a look at our last reciprocal function, cotx.
What is the antiderivative of cotx?
You may think that taking this integral requires the same trick as taking the antiderivative of secx and cscx, but it is actually different. Instead, finding the antiderivative of cotx only uses the u substitution (very similar to the antiderivative of tanx).
So setting up our integral we have:
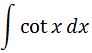
Note that cot x = cos x /sin x, so we can change our integral to
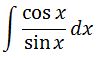
Now we can use u substitution. Let u = sinx. Then du = cosx dx, and substituting these will give us
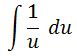
We have seen this many times, so evaluating this gives us that
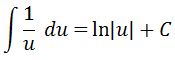
Recall that earlier we had u = sinx. So converting u back in terms of x leads to the final answer:
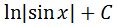
So much easier than integrating cscx and secx! See how the process was almost the same as the integral of tanx? Instead of substituting u=cosx, we did u=sinx here.
What is the antiderivative of cot^2?
The funny thing is that we already took the antiderivative of cot^2 before. We did it while we were trying to find the antiderivative of csc^2. Setting up our integral we have:
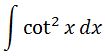
We know that cotx = cos x / sin x, so we can change our integral to
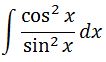
We need to use integration by parts here. Let
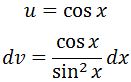
Then deriving u and integrating dv gives:
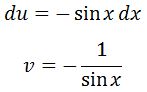
Plugging it in the integration by parts formula and evaluating will give us:
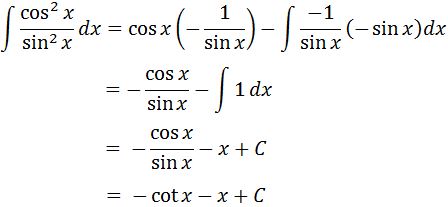
So the integral of cot^2x is –cotx-x+C. We have finally finished all the basic trig integrals, so let's take a look at trig integrals which requires the half angle identities.
What is the antiderivative of sin^2?
Setting up our integral we have
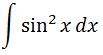
To integrate this, we are going to use the following half angle identity:
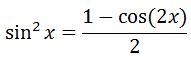
So we can change our integral to become:
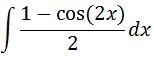
We can make the integral look at bit nicer by dividing 2 to each term independently, which gives us
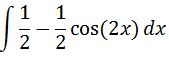
As you can see, this is pretty easy to integrate. Evaluating the integral will give us that:
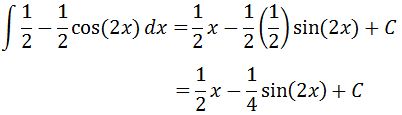
which is the integral of sin^2. Now let's take a look at another trig integral which utilizes the half angle identity.
What is the antiderivative of cos^2?
We want to find the integral of cos^2. In other words, let's evaluate the integral of
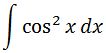
This time we are going to use the cos^2 half angle identity:
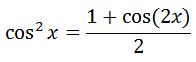
With this half angle identity, we can change our integral to
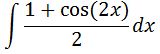
Again, we can make the integral look nicer by dividing 2 to each term independently, which gives us
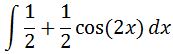
Evaluating the integral will give us:
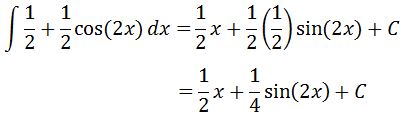
which is the integral of cos^2x.
To summarize, we have found the integral of 6 trig functions, as well as their integrals when each and one of them are squared.There is an endless amount of trig functions we can integrate. So if you are looking for an integral that you couldn't find in this article, then I suggest you look at this link.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_integrals_of_trigonometric_functions
Unfortunately it does not give you a step by step solution, but at least you will find the solution for your integral. In addition, there are also subjects we have not covered such as hyperbolic integrals. If you are interested in that, then you can take a look at this antiderivative chart at the very bottom.
http://math2.org/math/integrals/tableof.htm
Integral of lnx
Now that we are done with integrating trigonometric functions, let's take a look at the natural log. Before going right ahead to integral of the natural log, let's talk about what exactly ln is and what would integrating help us find.
What is lnx?
lnx is basically logarithm with base e of x. Another way of writing it would be
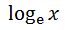
where e is a constant, and is approximated to be
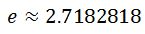
How do we graph this function? Well ln and the exponential function e^x are inverses of each other. So if you are able to graph e^x, then reflect it on the y=x line to get the graph of ln. Hence, the lnx graph will look like this:
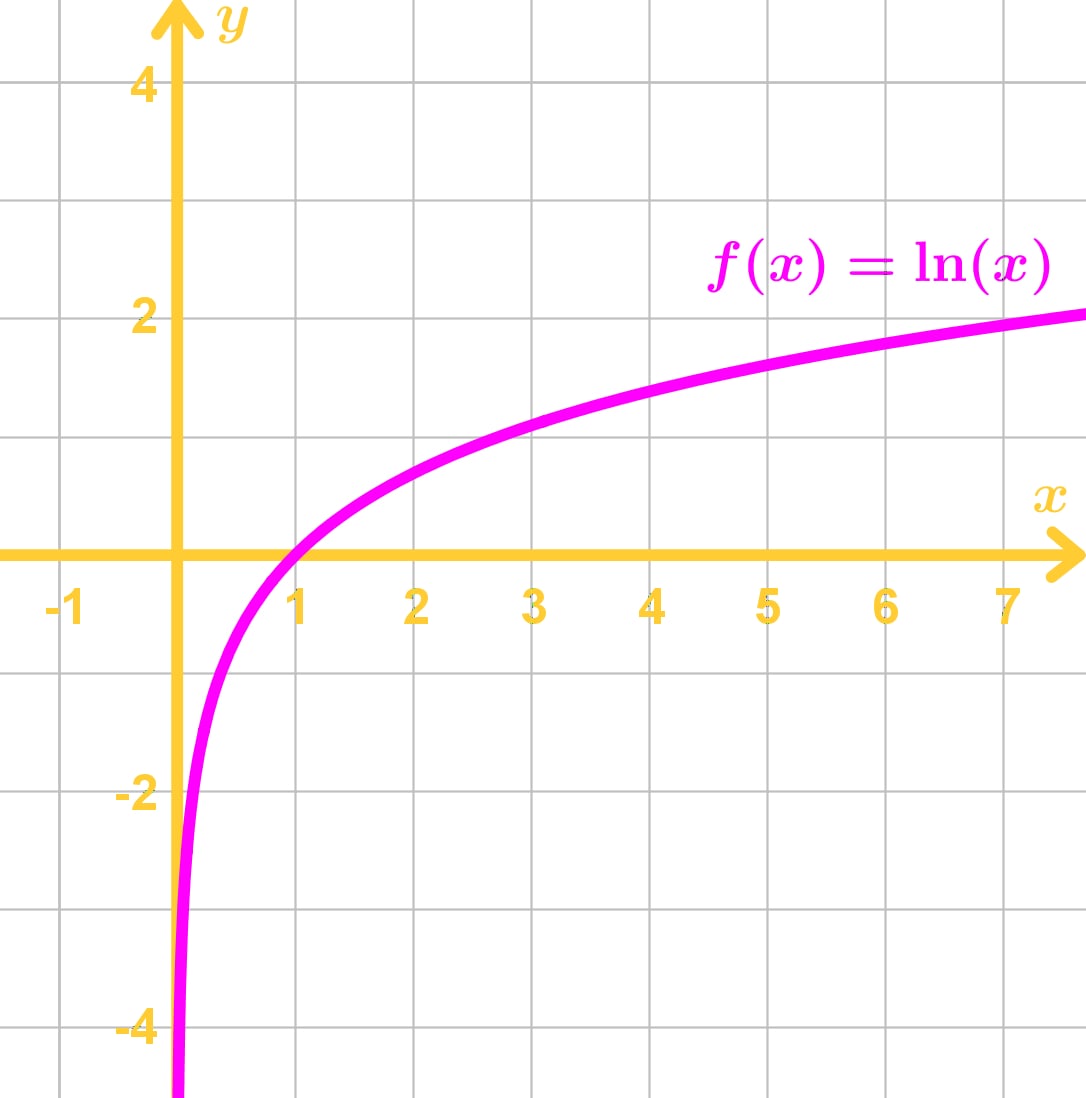
Notice that the only thing we can calculate in this graph without using a calculator is the ln of 1. We see that ln1 in the graph is 0. This is because we know that the logarithm of 1 with any base is 0.
The natural log is very interesting because they have very special rules. These ln rules involve the product rule, quotient rule, and power rule.
For the product rule, we are able to split a ln function into an addition of two ln functions if the inside of the logarithm is a product of 2 or more things. In other words,
Product Rule:ln(xy) = ln(x)+ln(y)
For the quotient rule, we are able to split a ln function into a subtraction of two ln functions if the inside of the logarithm is a quotient of 2 things. In other words,
Quotient Rule:ln(x/y) = ln(x)-ln(y)
For the power rule, we can bring down the power of the function inside the logarithm and put it as a coefficient outside of the logarithm. In other words,
Power Rule:ln(x^y)=yln(x)
These properties will be very useful when dealing with very complicating ln functions. Now that we know about ln very well, let's try to find the antiderivative of ln x.
What is the antiderivative of lnx?
First, we set up our integral of lnx:
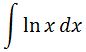
How do we integrate lnx? What's really hard to notice here is that you need to use integration by parts. Recall that the integration by parts formula is:
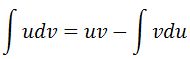
We set:
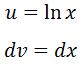
Deriving u and integrating dv will give us:
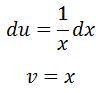
Plugging all four of these into the integration by parts formula gives us:
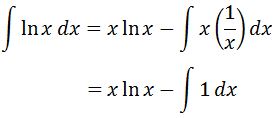
Notice that evaluating the integral of ln leads to the final answer:
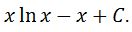
Be Sure to download the antiderivate table. It is very handy when you are studying, working on calculus assignments, or making a cheat sheet for your exams.






