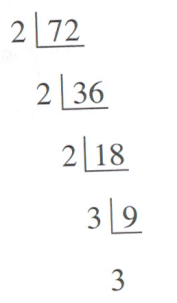Factor
One of the first things you'll need to learn about before tackling prime and composite numbers are factors. Factors are what you'll have to multiply together in order to get a certain number. So for example, the factors of 18 is 2 and 9 since 2 x 9 = 18. The divisor definition is a number that another number is to be divided with. In this case, 2 and 9 are each also known as a divisor.
Prime numbers
So what are prime numbers? Prime numbers are numbers that can only be factored by 1 and itself. An example of this is 2. You cannot get an answer of 2 in multiplication other than multiplying 2 with 1. 2 is known as a prime divisor.
Composite Numbers
Contrary to prime numbers, composite numbers are numbers that have more factors than just 1 and itself. It also is positive. For example, 9 can be factored into 3 x 3 or it can be 9 x 1. All whole numbers are either prime or composite, other than the number 1 and 0. 0 has an infinite amount of factors, whereas 1 cannot be made up of anything that is not itself.
Factor Tree
To tackle the questions in this lesson, you're going to have to learn about a factor tree. A factor tree breaks down a number so that you're able to identify its prime factors. The steps to making a factor tree is:
1) Write down the number you are trying to factorize at the top of the tree
2) Draw two branches stemming from the number downwards
3) Break down the original number into two factors and write it at the end of the branches you just drew in the previous step
4) Continue breaking down the numbers into factors at the end of branches until you're left with all prime numbers and there are no more factors to be found
5) Take all the numbers at the end of the factor tree branches to find out the prime factors of your original number
Continuous division
You can use a method called continuous division to find the greatest common factor (GCF) of a number. The GCF also deals with prime numbers. You can carry out continuous division by:
1) Writing down the two numbers you're trying to find the GCF of
2) Draw an "L" shape surrounding them
3) Divide both the numbers by a common factor
4) Write the answers you get underneath the bar
5) Continue doing this until all the numbers you're left with as answers are prime numbers
6) Multiply together all the numbers on the left hand side (that has been common factors of the numbers inside the "L") and you'll get your GCF
Example problems
Question 1:
1a) Factors of
Solution:
Since is not a prime number, we can break it down into two times two
We are done now because all the numbers are prime, but we can group up the same numbers in exponent form.
1b) Factors of
Solution:
And in exponent form
Question 2
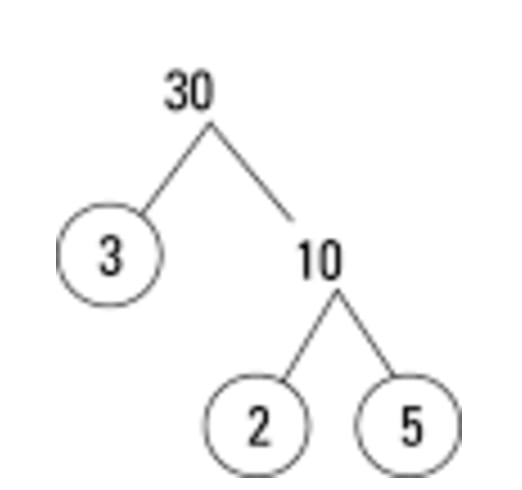
2a) Factors using factor tree
Solution:
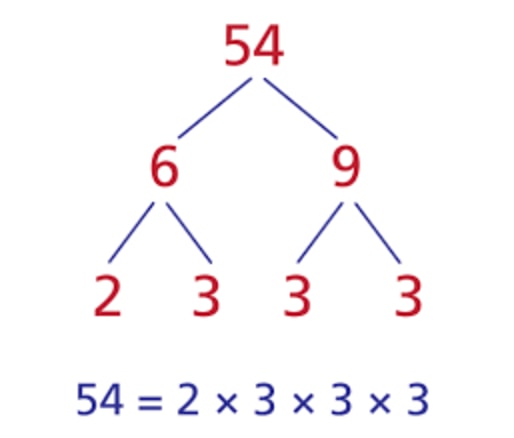
2b) Factors of using factor tree
Solution:
2c) Factors of , using tree
Solution:
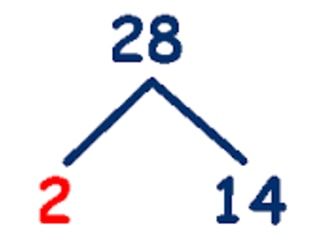
is not prime, so it can be factored further.
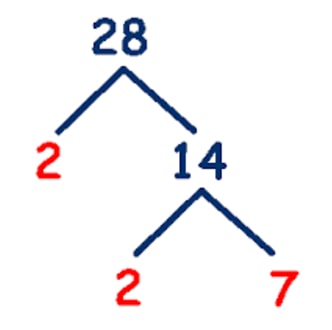
Question 3
What is the greatest common factor between and , using continuous division?
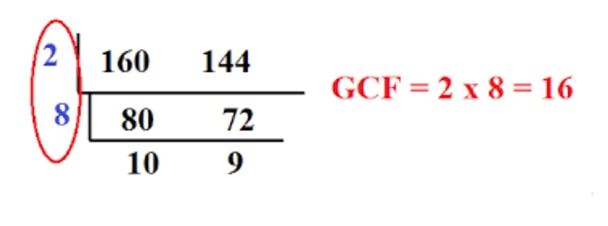
Got a number in mind you wanted to check the prime factors for? Here's a prime factor calculator you can check out.
Want to learn more related to this lesson? Take a look at how to use exponents to describe numbers, the product rule of exponents, how to find common factors of polynomials, and factoring polynomials.
Ex: The factor of 15 is 5 & 3. Because
Ex: 2,3,5,7,11,13,17…
Ex: 4,6,8…
Ex: Prime factors of
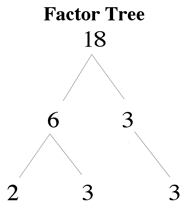
Ex: Prime factors of