Boost Your Year 10 Maths Grades
Step-by-step solutions that boost grades and confidence
Try Our Year 10 Maths Practice Test

📈
Math test scores improve 10-15%
✨
Problem-solving confidence
💡
Formula application mastery
📚
Mathematical concepts clarity

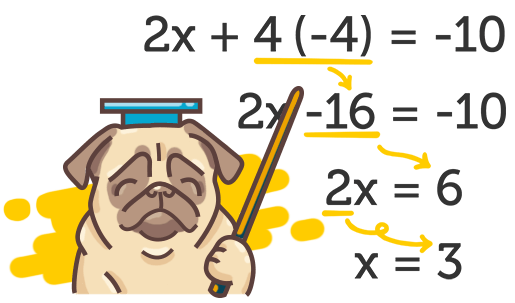
Step-by-Step Solutions
Understand equations, functions, and problem-solving

Perfect Curriculum Match
Aligned with National Curriculum requirements

Guaranteed Results
Most students improve one letter grade in 4-6 weeks
Change Courses
Year 10 Maths Topics
Number System and Radicals
Patterns and Solving Equations
Linear Equations (Basic)
Solving Linear Equations
Solving Linear Inequalities
Introduction to Relations and Functions
Linear Relations
Linear Functions
Solving Simultaneous Equations
Transformations of Functions
Exponents
Exponential Functions
Logarithmic Functions
Introduction to Polynomials
Multiplying and Dividing Polynomials
Operations of Polynomials
Factorising Polynomial Expressions
Factorising Polynomial (Advanced)
Quadratic Functions
Radicals
Algebraic Fractions
Reciprocal Functions
Scale Factors and Similarity
Properties of Triangles
Congruent Triangles
Pythagorean Theorem
Introduction to Surface Area of 3D Shapes
Introduction to Volume
Surface Area and Volume
Introduction to Trigonometry
Trigonometric Ratios and Angle Measure
Bearings
Graphing Trigonometric Functions
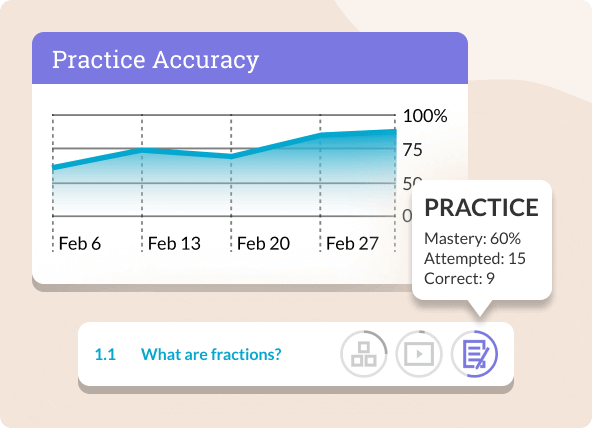
Introduction to Probability
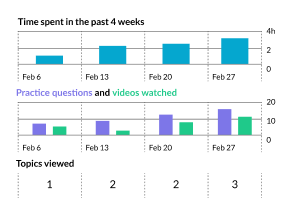
Data and Graphs
Introduction to Matrices
Determinants and Inverses of Matrices
Year 10 Maths FAQ
Unsure how StudyPug works? Need help with setting up? Check our frequently asked questions or contact us for help.
How does StudyPug help with Year 10 Maths?
Our video solutions break down Year 10 Maths step by step, making complex concepts easy to understand. Most students improve their grades within 30 days.
How does the subscription work?
Our subscription gives you full access to all Year 10 Maths content, including all video solutions, practice tests, worksheets, and quizzes. Choose monthly or annual plans.
What's included in my subscription?
Your subscription includes unlimited access to all Year 10 Maths video solutions, practice tests, worksheets, and quizzes. You'll get complete coverage of every topic in your curriculum.
Is StudyPug aligned with curriculum for Year 10 Maths?
Yes! Our content follows the Australian National Curriculum exactly, covering every topic and problem type required for Year 10 Maths.
How quickly will I improve in Year 10 Maths?
Most students see improved understanding within the first week. The majority report better test scores within 2-4 weeks of consistent practice.
Can StudyPug help with Year 10 Maths exams?
Absolutely! Our content covers all exam topics, with practice questions similar to those in actual exams. Many students report significant score improvements.
How do you explain difficult maths concepts?
We use visual aids, real-life examples, and step-by-step explanations to break down complex concepts. Our approach helps students understand the 'why' behind each solution.
Can I access StudyPug on different devices?
Yes! StudyPug works on computers, tablets, and smartphones. You can study anytime, anywhere, on any device with internet access.
Do you offer help for other year levels?
Yes, we cover maths for all high school years, from Year 7 to Year 12, including advanced topics for university preparation.
How does StudyPug compare to a maths tutor?
StudyPug offers 24/7 access to explanations and practice at a fraction of the cost of a private tutor. Many students use StudyPug alongside tutoring for optimal results.